"If we interpet the "bond" of the chemists as indicating a unit Faraday tube, connecting charged atoms in the molecule, the structural formulae of the chemist can be at once translated into the electrical theory . . . but the symbol indicating a bond on the chemical theory is not regarded as having direction, no difference is made on this theory between one end of the bond and the other. On the electrical theory, however, there is a difference between the ends, as one corresponds to a positive, the other to a negative charge."
J.J. Thomson in Electricity and Matter
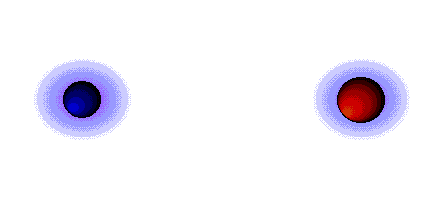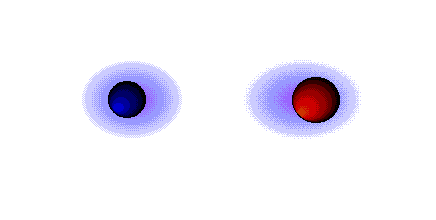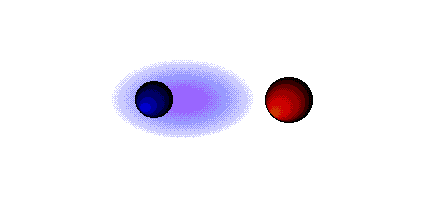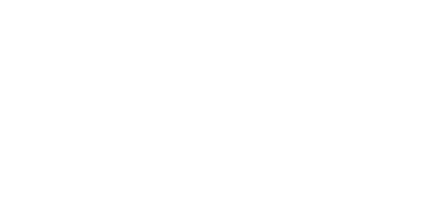
1. diferença de electronegatividade inferior a 1.6, a ligação é considerada covalente;
2. diferença de electronegatividade superior a 2.0, a ligação é considerada iónica.
O que acontece quando a diferença de electronegatividade está compreendida no intervalo 1.6 a 2.0?
3. se a diferença de electronegatividade é 1.6-2.0, a ligação é considerada covalente se apenas não metais estiverem envolvidos; se um metal estiver envolvido então a ligação é considerada iónica.
2002 Palmira Silva